Lublin Info Centre
Robotics and automation in SME: Eastern Poland’s path to Industry 4.0

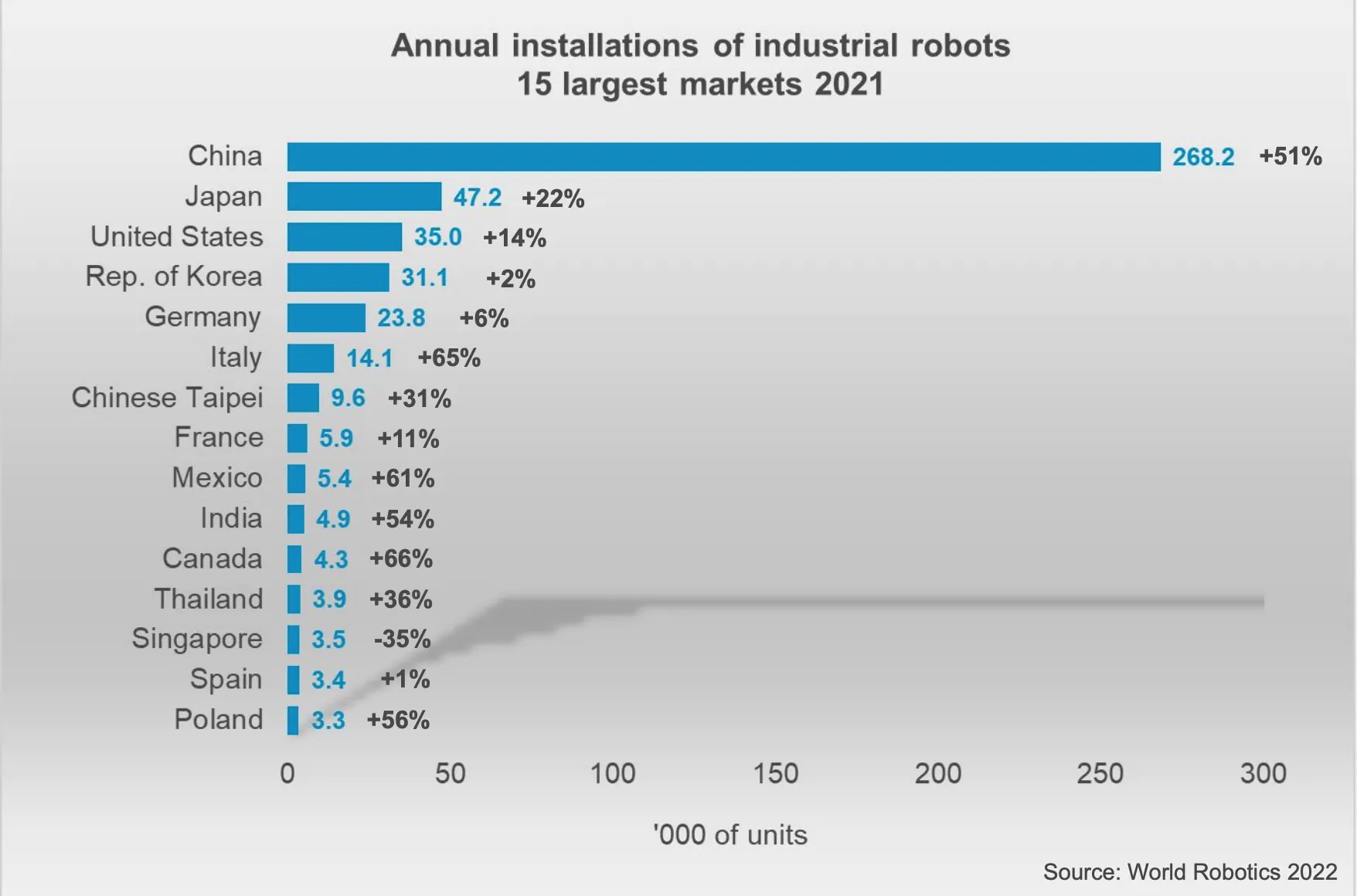
Although Poland has made significant progress in adopting new technologies within business, it still lags behind its global counterparts. As indicated in the report by the Sobieski Institute titled “Truly Digital Poland – Industrial Automation and Robotics,” South Korea boasts 1000 industrial robots per 10,000 employees, Germany uses 397, while Poland utilizes only 52. On a global scale, the average is 141 robots per 10,000 employees. To bridge this gap, integrating robots into production processes is essential, not just on a mechanical level. This transition isn’t about replacing human labour with machines, but rather about enhancing a company’s technological capabilities and fostering collaboration within the global market.
The integration of robotics into various industries is undoubtedly a complex task, requiring careful planning, technological expertise, and most importantly significant financial investments, which make this possibility out of reach for some companies. The significant costs associated with acquiring advanced robotics technology, restructuring infrastructure, and training a skilled workforce can often present considerable barriers for many businesses, especially smaller and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Acknowledging these challenges the European Funds for Eastern Poland programme 2021-2027 continues the aid for eastern provinces to speed up their growth. On August 2nd, the application process for Measure 1.2: Automation and Robotization in SMEs under the European Funds for Eastern Poland, organized by the Polish Agency for Enterprise, has been launched. The program’s primary objective is to facilitate the transformation of businesses towards Industry 4.0 by encouraging automation and robotization of processes.
What is Industry 4.0 and how it is impacting business?
The central idea here revolves around companies evolving into Industry 4.0 – but what exactly does this mean and how can it be described?
Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of digital technologies like AI, IoT, and automation into manufacturing and industry. It’s revolutionizing businesses by enhancing efficiency, quality, and innovation through real-time data, smart machines, and improved connectivity. This leads to higher productivity, better products, and new business opportunities. It also requires upskilling the workforce and prioritizing cybersecurity. Overall, Industry 4.0 is reshaping industries for greater competitiveness and sustainability.
Automation and Robotization in SMEs – about the programme
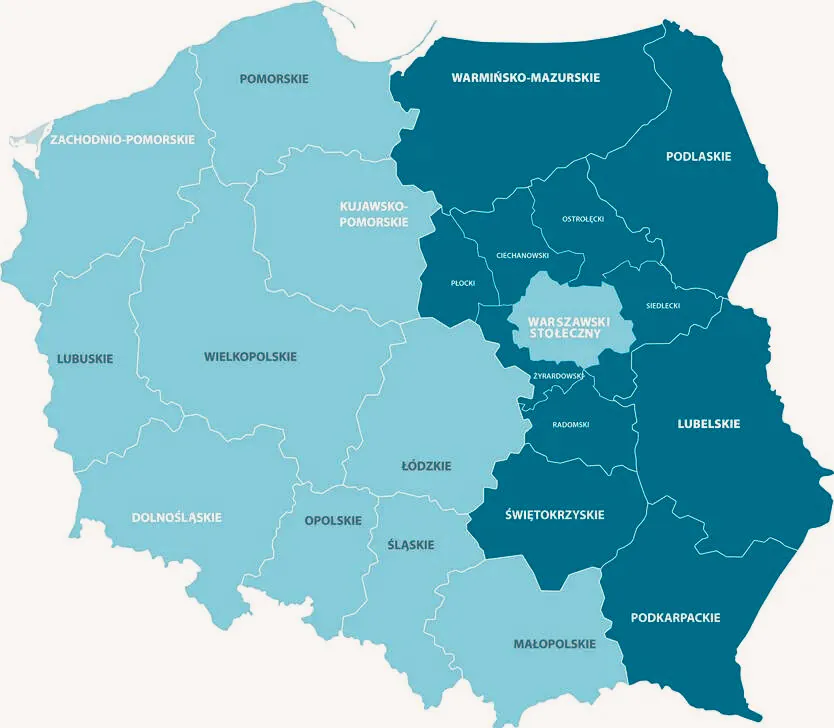
The programme aims at strengthening the conditions for improving the competitiveness of the economy and quality of life in six provinces in eastern Poland: Warmińsko-Mazurskie, Podlaskie, Lubelskie, Świętokrzyskie, Podkarpackie and Mazowieckie (excluding Warsaw and the surrounding municipalities).
Application period: August 2, 2023 – October 25, 2023
Funding: depending on the project’s scope:
De minimis aid – 85%
Regional aid – micro and small companies 70%, medium-sized companies 60%.
The competition does NOT apply to large companies.
The minimum value of eligible costs is 200,000.00 PLN
The maximum funding amount is 3,000,000.00 PLN
The funding can be allocated for the following purposes:
- Conducting a technological audit and developing a roadmap for the company’s transition towards Industry 4.0.
- Implementing investment activities, including the purchase of robots, automation equipment, and software.
- Providing support for the installation and implementation process through training and advisory services.
The project must align with the scope and purpose of the initiative, involving the acquisition and implementation of at least one of the following:
- Industrial robot – an automated manipulator, whether stationary or mobile, programmable in three or more axes. It is designed to automate industrial processes within the company’s technological operations.
- Autonomous service robot. This category does not include robots used in the automation of fundamental industrial processes. Autonomy refers to the scope of a robot’s actions (e.g., the movement of mobile robots within a production facility) where specific functions are controlled by a computer system based on data gathered from sensors, without the need for direct human intervention.
Roadmap
A crucial requirement is the creation of a “roadmap.” Optimizing automation and robotization processes involves deliberate and planned purchases guided by this roadmap. The roadmap outlines the entire investment plan or the process of aligning the company with Industry 4.0 requirements. It is based on an audit and diagnosis of the company’s digital maturity. Importantly, the audit must be conducted before submitting the application and should be attached along with the investment plan (the “roadmap”). Notably, SMEs can also access EU support for financing services like advisory assistance, audits, and roadmap preparation.
The development of these roadmaps will receive assistance from European Digital Innovation Hubs (EDIHs), entities equipped with digitization expertise. They play a crucial role in offering free support to companies facing diverse challenges related to digital transformation. The EDIH network is currently being established in Poland, with the European Commission having already selected the initial EDIH consortia in the country.
Funding will encompass expenses related to:
- Costs of advisory services related to conducting a technological audit/digital maturity assessment of the enterprise and developing a roadmap,
- Costs of advisory services necessary for implementing the roadmap,
- Acquisition of tangible assets, excluding constructed and unconstructed real estate,
- Purchase of software or other intangible assets and legal rights in the form of patents, licenses, know-how, and other intellectual property,
- Costs of training services,
- Costs of robotics and construction materials directly linked to the installation of machinery and equipment.
- Costs of establishing and maintaining security for an advance payment in the project.
The ultimate goal of the funded projects is to drive business process innovation within the enterprises, particularly by automating and robotizing production processes. By embracing Industry 4.0 principles, SMEs in Eastern Poland can become more efficient, competitive, and technologically advanced, paving the way for sustainable growth and development in the region.






